Christopher P. Hill
Distinguished Professor of Biochemistry
Vice Dean for Research, School of Medicine
Protein Structure and Function
Molecular Biology Program
Biological Chemistry Program
Education
B.A. University of York, United Kingdom
D.Phil. University of York, United Kingdom
Research
We study how macromolecular complexes assemble, move, and function to perform important biological processes. We use a range of molecular biological and biochemical techniques, with a major focus on determining 3-D structures by X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy. Our interests include HIV, nucleosome remodeling and reorganization, proteasome activation, and molecular machines called AAA ATPases.
Some of our recent studies and consequent understanding of AAA ATPase mechanism is illustrated in the figure on the basis of our work on Vps4. The active Vps4 complex, whose structure is illustrated in the left-hand panel of the figure, comprises six Vps4 subunit, six dimers of the Vta1 cofactor protein, and a peptide substrate. The substrates are ESCRT-III proteins, which form filamentous assemblies that drive membrane fission for many membrane fission events, including the final steps of cell division and the budding of many viruses, including HIV. As shown in the middle panels, our structural and biochemical studies show how Vps4 binds to ESCRT-III by binding the side chains in an alternating series of type I and type II binding sites. This provides the key to understanding how this remarkable enzyme translocates ESCRT-III subunits through the pore of the Vps4 hexamer, thereby unfolding them and causing the ESCRT-III filaments to disassemble. These studies also explain how many other AAA ATPases function in a very wide range of essential biological processes. The mechanism is illustrated in the right-hand panel. Five of the Vps4 subunits form a helix that is stabilized by binding of ATP and matches the symmetry of an extended, unfolded polypeptide substrate. Hydrolysis of ATP at the bottom end of the Vps4 helix allows the subunit to move from the bottom end to release ADP, rebind ATP, and join the top end of the Vps4 helix. In doing so, the Vps4 hexamer walks along the ESCRT-III protein forcing it into an extended conformation, which in turn leads to the biological response.
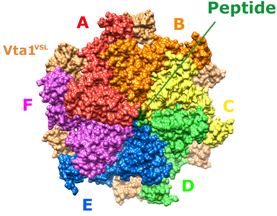
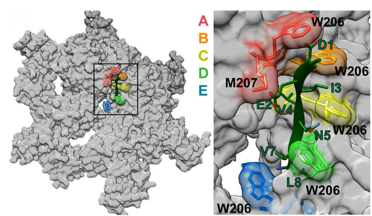
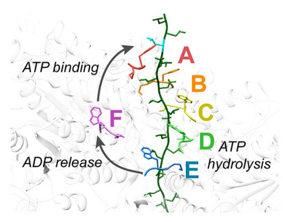
Left - Structure of the active Vps4 complex. Middle – Details of peptide binding. Right – Mechanism.
References
- Kessler JL, Kang G, Qin Z, Kang H, Whitby FG, Cheatham TE 3rd, Hill CP, Li Y, Yu SM. (2021) Peptoid Residues Make Diverse, Hyperstable Collagen Triple-Helices. J Am Chem Soc. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c00708. [Online ahead of print]
- Tsai FTF, Hill CP. (2020) Same structure, different mechanisms? Elife 9:e56501.
- Xiong X, Blakely A, Karra P, VandenBerg MA, Ghabash G, Whitby F, Zhang YW, Webber MJ, Holland WL, Hill CP, Chou DH. (2019) Novel four-disulfide insulin analog with high aggregation stability and potency. Chem Sci. 11:195-200
- Cooney I, Han H, Stewart MG, Carson RH, Hansen DT, Iwasa JH, Price JC, Hill CP, Shen PS. (2019) Structure of the Cdc48 segregase in the act of unfolding an authentic substrate. Science. pii: eaax0486. [Epub ahead of print]
- Han H, Fulcher JM, Dandey VP, Iwasa JH, Sundquist WI, Kay MS, Shen PS, Hill CP. (2019) Structure of Vps4 with circular peptides and implications for translocation of two polypeptide chains by AAA+ ATPases. Elife.8. pii: e44071.
- Chun Y, Joo YJ, Suh H, Batot G, Hill CP, Formosa T, Buratowski S. (2019) Selective kinase inhibition shows that Bur1 (Cdk9) phosphorylates the Rpb1 linker in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. MCB.00602-18. [Epub ahead of print]
- Hemmis CW, Heard SC, Hill CP. (2019) Phosphorylation of Tyr-950 in the proteasome scaffolding protein RPN2 modulates its interaction with the ubiquitin receptor RPN13. J Biol Chem. 294:9659-9665.
- Han H, Hill CP. (2019) Structure and mechanism of the ESCRT pathway AAA+ ATPase Vps4. Biochem Soc Trans. 47:37-45.
- Zurita Rendón O, Fredrickson EK, Howard CJ, Van Vranken J, Fogarty S, Tolley ND, Kalia R, Osuna BA, Shen PS, Hill CP, Frost A, Rutter J. (2018) Vms1p is a release factor for the ribosome-associated quality control complex. Nat Commun. 2018 Jun 6;9(1):2197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04564-3.
- Han H, Monroe N, Sundquist WI, Shen PS, Hill CP (2017) The AAA ATPase Vps4 binds ESCRT-III substrates through a repeating array of dipeptide-binding pockets. Elife. 2017 Nov 22;6. pii: e31324. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31324.
- Nielson JR, Fredrickson EK, Waller TC, Rendón OZ, Schubert HL, Lin Z, Hill CP, Rutter J (2017) Sterol Oxidation Mediates Stress-Responsive Vms1 Translocation to Mitochondria. Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.
- Sdano MA, Fulcher JM, Palani S, Chandrasekharan MB, Parnell TJ, Whitby FG, Formosa T, Hill CP. (2017) A novel SH2 recognition mechanism recruits Spt6 to the doubly phosphorylated RNA polymerase II linker at sites of transcription. Elife. 2017 Aug 16;6. pii: e28723. doi: 10.7554/eLife.28723.
- VanderLinden RT, Hemmis CW, Yao T, Robinson H, Hill CP. (2017) Structure and energetics of pairwise interactions between proteasome subunits RPN2, RPN13, and ubiquitin clarify a substrate recruitment mechanism. J Biol Chem. 292(23):9493-9504.
- Monroe N, Han H, Shen PS, Sundquist WI, Hill CP. (2017) Structural basis of protein translocation by the Vps4-Vta1 AAA ATPase. Elife. Apr 5;6. pii: e24487. doi: 10.7554/eLife.24487.
- Monroe N, Hill CP. (2016) Meiotic Clade AAA ATPases: Protein Polymer Disassembly Machines. J Mol Biol. 428:1897-911.
- Kemble DJ, McCullough LL, Whitby FG, Formosa T, Hill CP. (2015) FACT Disrupts Nucleosome Structure by Binding H2A-H2B with Conserved Peptide Motifs. Mol Cell. 60:294-306.
- Han H, Monroe N, Votteler J, Shakya B, Sundquist WI, Hill CP. (2015) Binding of Substrates to the Central Pore of the Vps4 ATPase Is Autoinhibited by the Microtubule Interacting and Trafficking (MIT) Domain and Activated by MIT Interacting Motifs (MIMs). J Biol Chem 290:13490-9.
- VanderLinden RT, Hemmis CW, Schmitt B, Ndoja A, Whitby FG, Robinson H, Cohen RE, Yao T, Hill CP. (2015) Structural basis for the activation and inhibition of the UCH37 deubiquitylase. Molecular Cell 57:901-11.
- Monroe N, Han H, Gonciarz MD, Eckert DM, Karren MA, Whitby FG, Sundquist WI, Hill CP. (2014) The oligomeric state of the active Vps4 AAA ATPase. J Mol Biol 426:510-25.
- Hill CP, Sundquist WI. (2013) Building a super elongation complex for HIV. Elife 2:e00577.
- Kemble DJ, Whitby FG, Robinson H, McCullough LL, Formosa T, Hill CP. (2013) Structure of the Spt16 middle domain reveals functional features of the histone chaperone FACT. J Biol Chem. 288:10188-94.
- Kish-Trier E, Hill CP. (2013) Structural biology of the proteasome. Annu Rev Biophys 42:29-49.
- Schubert HL, Wittmeyer J, Kasten MM, Hinata K, Rawling DC, Héroux A, Cairns BR, Hill CP. (2013) Structure of an actin-related subcomplex of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeler. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:3345-50.
- Stadtmueller BM, Kish-Trier E, Ferrell K, Petersen CN, Robinson H, Myszka DG, Eckert DM, Formosa T, Hill CP. (2012) Structure of a proteasome Pba1-Pba2 complex: implications for proteasome assembly, activation, and biological function. J Biol Chem 287:37371-82.
- Tian G, Park S, Lee MJ, Huck B, McAllister F, Hill CP, Gygi SP, Finley D. (2011) An asymmetric interface between the regulatory and core particles of the proteasome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:1259-67.
- Zhang H, Constantine R, Vorobiev S, Chen Y, Seetharaman J, Huang YJ, Xiao R, Montelione GT, Gerstner CD, Davis MW, Inana G, Whitby FG, Jorgensen EM, Hill CP, Tong L, Baehr W. (2011) UNC119 is required for G protein trafficking in sensory neurons. Nat Neurosci 14:874-80.
- Stadtmueller BM, Hill CP. (2011) Proteasome activators. Molecular Cell 41:8-19.
- McDonald SM, Close D, Xin H, Formosa T, Hill CP. (2010) Structure and biological importance of the Spn1-Spt6 interaction, and its regulatory role in nucleosome binding. Molecular Cell 40:725-735.
- Schubert HL, Zhai Q, Sandrin V, Eckert DM, Garcia-Maya M, Saul L, Sundquist WI, Steiner RA, Hill CP. (2010) Structural and functional studies on the extracellular domain of BST2/tetherin in reduced and oxidized conformations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:17951-17956
- Sadre-Bazzaz K, Whitby FG, Robinson H, Formosa T, Hill CP. (2010) Structure of a Blm10 complex reveals common mechanisms for proteasome binding and gate opening. Molecular Cell 37:728-35.
- Pornillos O, Ganser-Pornillos BK, Kelly BN, Hua Y, Whitby FG, Stout CD, Sundquist WI, Hill CP, Yeager M. (2009) X-ray structures of the hexameric building block of the HIV capsid. Cell 137:1282-92.
- Bajorek M, Schubert HL, McCullough J, Langelier C, Eckert DM, Stubblefield WB, Uter NT, Myszka DG, Hill CP, Sundquist WI. (2009) Structural Basis for ESCRT-III Protein Autoinhibition. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:754-62.
- McCullough J, Fisher RD, Whitby FG, Sundquist WI, Hill CP. (2008) ALIX-CHMP4 interactions in the human ESCRT pathway. PNAS 105:7687-91.
- Zhai Q, Fisher RD, Chung HY, Myszka DG, Sundquist WI, Hill CP. (2008) Structural and functional studies of ALIX interactions with YPX(n)L late domains of HIV-1 and EIAV. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15:43-9.
- Fisher RD, Chung H-Y, Zhai Q, Robinson H, Sundquist WI Hill CP. (2007) Structural and Biochemical Studies of ALIX/AIP1 and Its Role in Retrovirus Budding. Cell 128:841-52.
- Alam SL, Langelier C, Whitby FG, Koirala S, Robinson H, Hill CP, Sundquist WI. (2006) Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition by the human ESCRT-II EAP45 GLUE domain. Nature Structural Molecular Biology 13:1029-30.
- VanDemark AP, Blanksma M, Ferris E, Heurox A, Hill CP, Formosa T. (2006) The Structure of the yFACT Pob3-M Domain, Its Interaction with the DNA Replication Factor RPA, and a Potential Role in Nucleosome Deposition. Molecular Cell 22:363–374.
- Macbeth MR, Schubert HL, VanDemark AP, Ligam AT, Hill CP,Bass BL. (2005) Inositol hexakisphosphate is bound in the ADAR2 core and required for RNA editing. Science 309(5740):1534-1539.
- Forster A, Masters EI, Whitby FG, Robinson H, Hill CP. (2005) Implications for proteasome - PAN/PA 700 interactions from the 1-9A structure of a proteasome -11S activator complex. Molecular Cell 18:589-99.
- Sundquist WI, Schubert HL, Kelley BN, Hill GC, Holton JM, Hill CP. (2004) Ubiquitin Recognition by the Human TSG101 Protein. Molecular Cell 13:783-9.
