Scott Summers
Professor and Chair of Nutrition and Integrative Physiology and Adjunct Professor of Biochemistry
Co-Director of the Diabetes and Metabolism Research Center
Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, Metabolic Disease, Sphingolipids, Ceramide, Insulin Resistance and Beta Cell Failure

Molecular Biology Program
Biological Chemistry Program
Education
B.S. Indiana University
Ph.D. Southern Illinois University
Research
Ceramides are products of fat and protein metabolism that accumulate in individuals prone to metabolic disorders. Once ceramide levels rise above a critical threshold, tissues become unresponsive to insulin, the hormone that facilitates nutrient storage. The Summers Laboratory found that implementing pharmacological or genetic engineering strategies to block ceramide accumulation in rodents improves insulin sensitivity and prevents the onset of diabetes and fatty liver disease. Building upon these discoveries, they now seek to understand the regulatory mechanisms governing ceramide synthesis or action and to identify new therapeutic strategies for reducing ceramides to treat these pathologies.
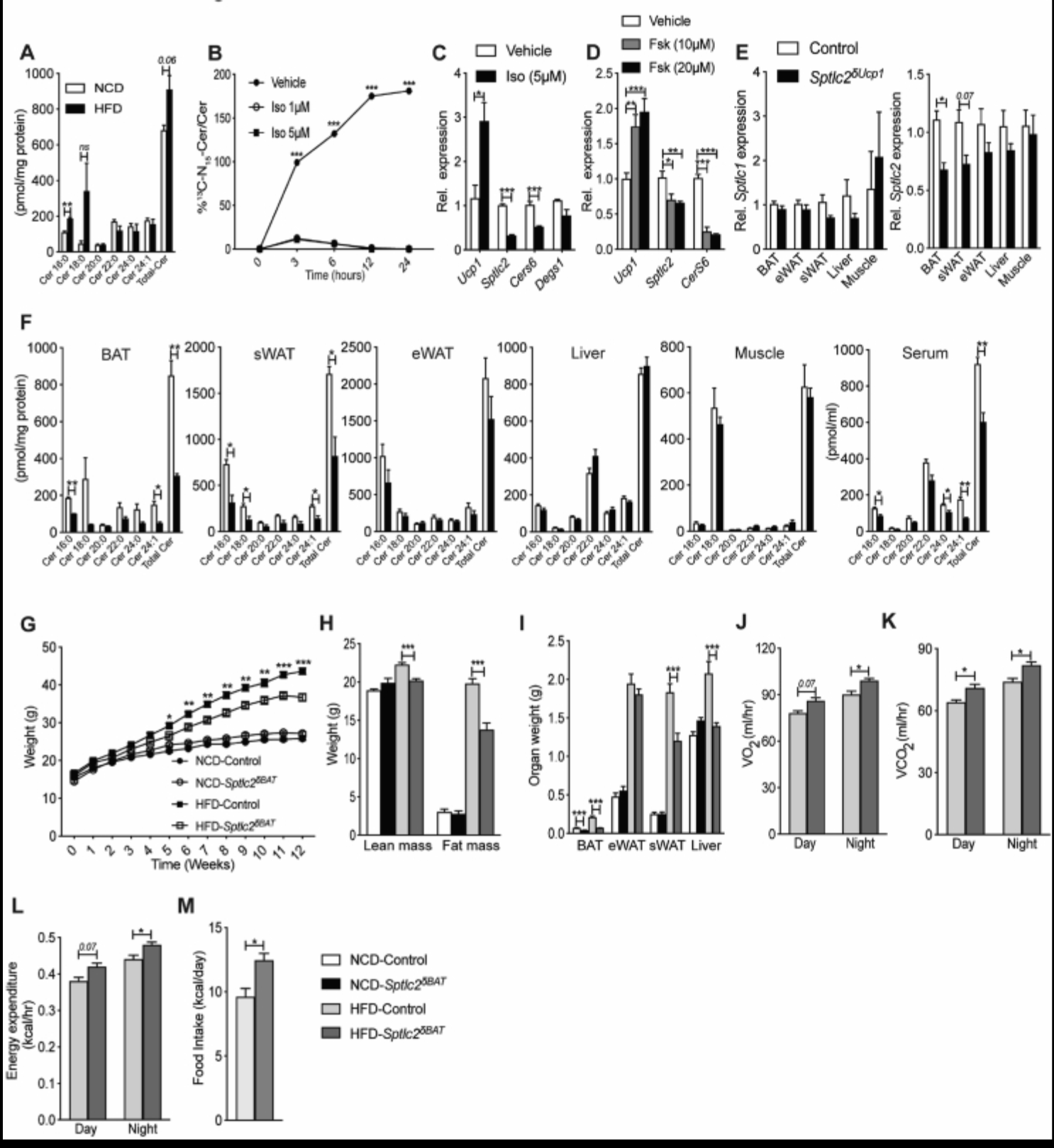
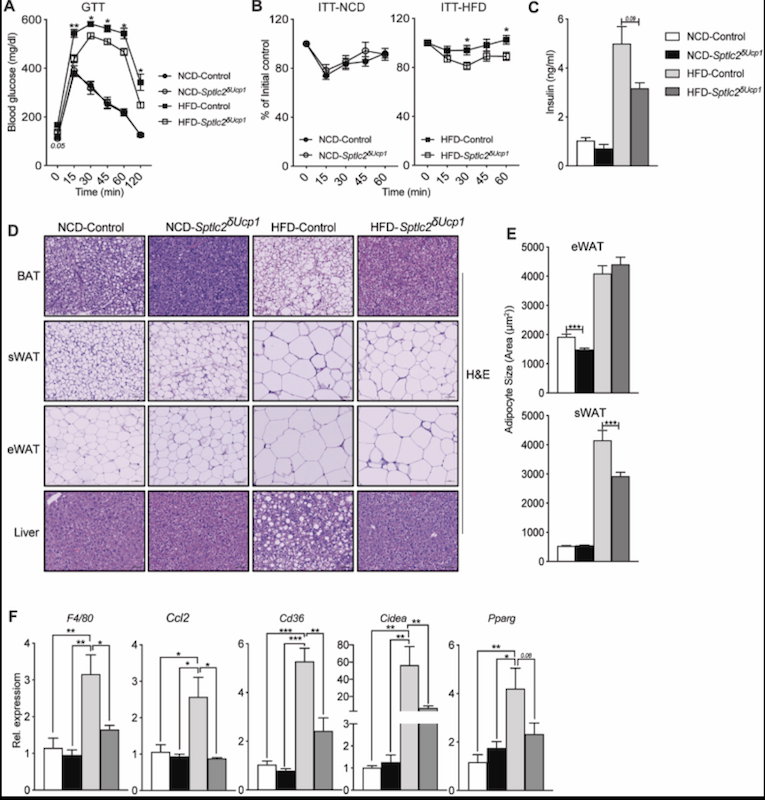
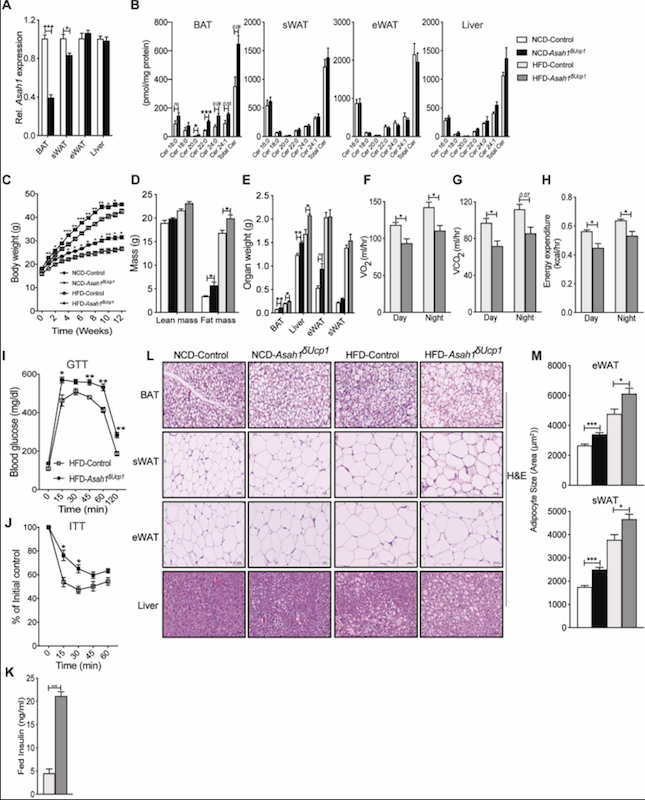
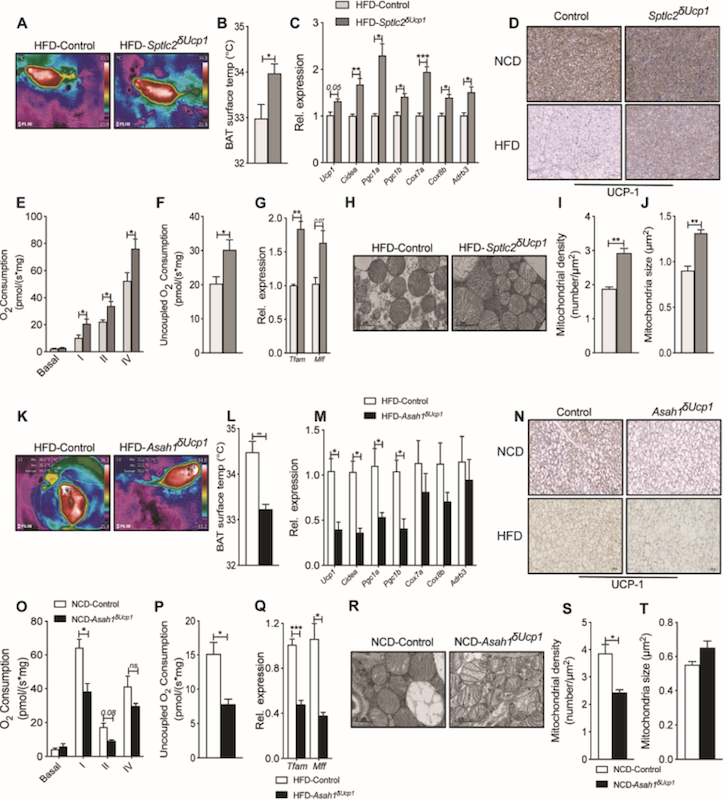
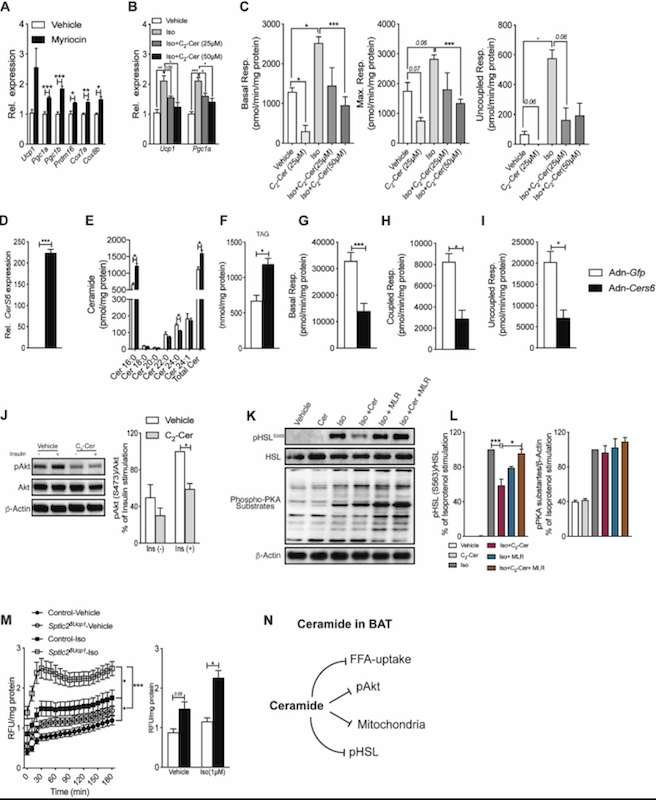
Ceramides are necessary and sufficient for diet-induced impairment of thermogenic adipocytes
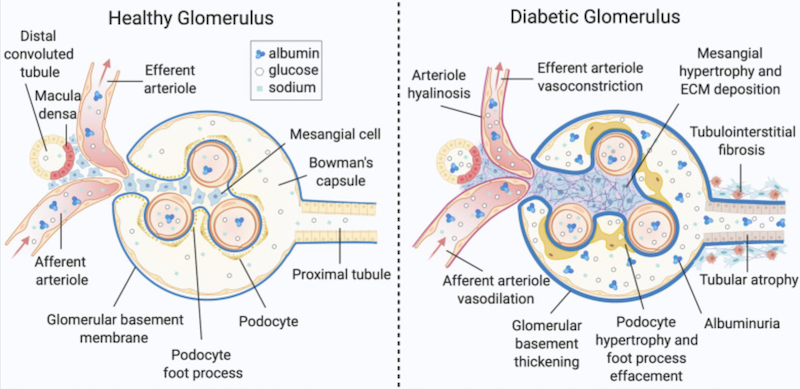
Rotten to the Cortex: Ceramide-Mediated Lipotoxicity in Diabetic Kidney Disease
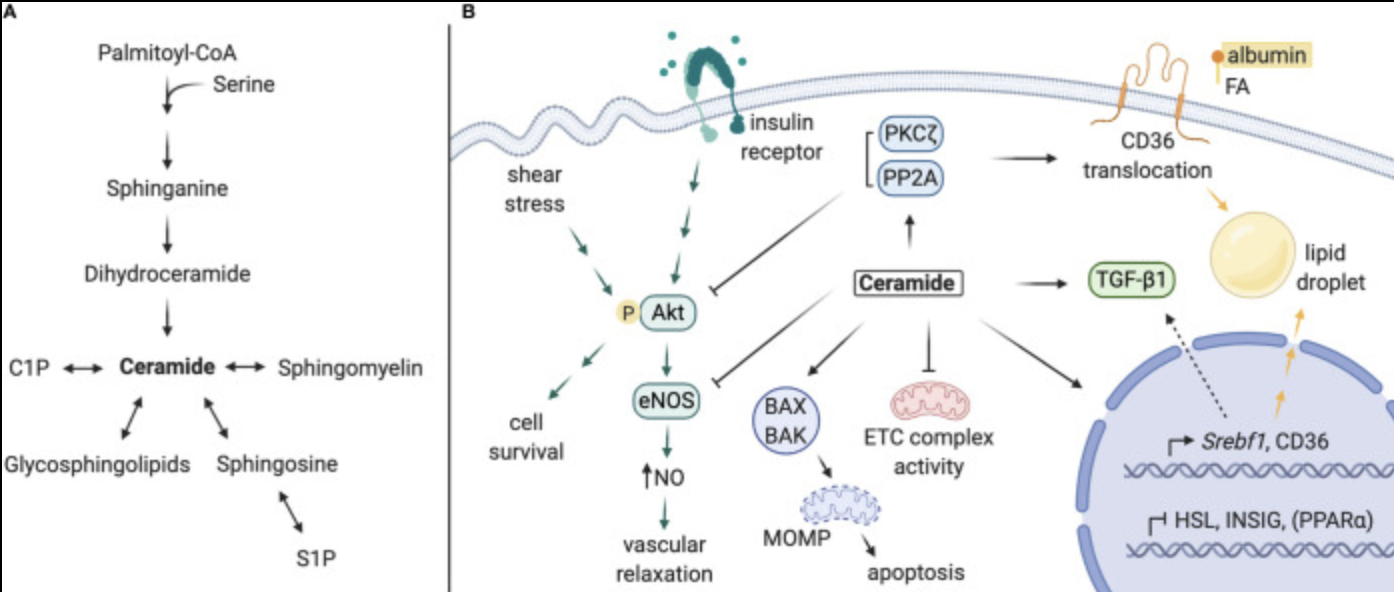
References
- Li Y, Chaurasia B, Kaddai V, Wilkerson JL, Maschek JA, Cox J, Wei P, Bensard C, Meikle PJ, Clevers H, Shayman JA, Hirabayashi Y, Holland WL, Rutter J, Summers SA (2023) "Ceramides increase fatty acid utilization in intestinal progenitors to enhance stemness and increase tumor risk.” Gastroenterology (in press)
- Nicholson RJ, Holland WL, Summers SA. (2022) Ceramides and Acute Kidney Injury. Seminars in Nephrology 42(3, 151281)
- Nicholson RJ, Norris MK, Poss AM, Holland WL, Summers SA. (2022) The Lard Works in Mysterious Ways: Ceramides in Nutrition-Linked Chronic Disease. Annu Rev Nutr. 42, 115-144.
- Poss AM, Krick B., Maschek JA, Haaland B., Cox JE, Karra P, Ibele AR, Hunt SC, Adams TD, Playdon MC, Holland WL, and Summers SA (2022) Following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, high serum ceramides demarcate patients that will fail to achieve sustained normoglycemia and diabetes remission. Med (NY) 3(7), 452-467
- Holland WL, Brozinick JT, Wang LP, Hawkins ED, Sargent KM, Liu Y, Narra K, Hoehn KL, Knotts TA, Siesky A, Nelson DH, Karathanasis SK, Fontenot GK, Birnbaum MJ and Summers SA (2007) Inhibition of ceramide synthesis ameliorates glucocorticoid-, saturated-fat-, and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metabolism 5(3), 167-79
- Holland WL, Miller R, Wang ZV, Barth, B, Bui, HH, Halberg, N, Davis, KE, Wade, M, Kuo, M-S, Brozinick, JT, Zhang, BB, Birnbaum, MJ, Summers SA, and Scherer PE (2011) A unifying mechanism for adiponectin Action: the pleiotropic actions of adiponectin are mediated via receptor-mediated activation of neutral ceramidase activity. Nature Medicine 17(1), 55-63
- Holland WL, Bikman BT, Wang L-P, Sargent KM, Knotts TA, Shui G, Wenk MR, Pagliassotti MJ and Summers SA (2011)Lipid-induced insulin resistance mediated by the proinflammatory receptor TLR4 requires saturated fatty acid-induced ceramide biosynthesis in mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation 121(5), 1858-70
- Bikman BT and Summers SA (2011) Ceramides as modulators of cellular and whole-body metabolism. Journal of Clinical Investigation 11, 4222-4230
- Chavez JA and Summers SA (2012) A ceramide-centric view of insulin resistance and lipotoxicity. Cell Metabolism 15(5), 585-94
- Siddique MM, Ying L, Wang L-P, Ching J, Mal M, Ilkayeva O, Ya JW, Boon HB and Summers SA (2013) Ablation of dihydroceramide desaturase 1, a therapeutic target for the treatment of metabolic diseases, simultaneously stimulates anabolic and catabolic signaling. Molecular and Cellular Biology 33, 2353-2369
- Chavez JA, Siddique MM, Wang ST, Ching J, Shayman JA, and Summers SA (2014) Ceramides and Glucosylceramides are Independent Antagonists of Insulin Signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry 289(2),723-34
- Raichur S, Wang ST, Chan PW, Li Y, Ching J, Chaurasia B, Dogra S, Öhman M, Takeda K, Sugii S, Pewzner-Jung Y, Futerman AH, Summers SA (2014) Increases in C16:0 Ceramides Resulting From CerS2 Haploinsufficiency Inhibits b-Oxidation and Confers Susceptibility to Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Insulin Resistance. Cell Metabolism 20(4), 687-95
- Siddique M, Li Y, Chaurasia B, Kaddai V and Summers SA (2015) Dihydroceramides – From bit players to lead actors. Journal of Biological Chemistry 290(25), 15371-9
- Summers SA (2015) The ART of lowering ceramides. Cell Metabolism 22(2), 195-6
- Chaurasia B and Summers SA (2015) Ceramides—Lipotoxic inducers of metabolic disorders. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism 26(10):538-50
- Summers SA and Goodpaster B (2016) CrossTalk Proposal: Intramyocellular ceramides do cause insulin resistance. Journal of Physiology 594(12), 316703170
- Summers SA and Goodpaster B (2016) Rebuttal to CrossTalk Proposal: Intramyocellular ceramides do not cause insulin resistance. Journal of Physiology 594(12), 3167-3170
- Park M, Kaddai V, Ching J, Fridianto KT, Sieli RJ, Sugii S, Summers SA (2016) Role for Ceramides, but NOT Sphingomyelins, as antagonists of insulin signaling and mitochondrial metabolism in C2C12 myotubes. Journal of Biological Chemistry 291 (46), 23978-23988
- Chaurasia B, Kaddai VA, Lancaster GL, Henstridge DC, Srirah S, Galam DAL, Gopalan, V, BPrahkash KNB, Velan SS, Bulchand S, Tson TJ, Wang M, Siddique MM, Yuguang G, Sigmundsson K, Mellet NA, Weir JM, Meikle PJ, Shabeeer BMMY, Shabbir A, Shayman JA, Hirabahashi Y, Shio SATE, Sugii S, and Summers SS (2016) Adipocyte ceramides regulate subcutaneous adipose browning, inflammation and metabolism 24(6), 820-843
- Meikle PJ and Summers SA (2017) Sphingolipids and phospholipids in insulin resistance and related metabolic disorders. Nature Reviews in Endocrinology and Metabolism 13(2), 79-91
- Summers SA (2018) Could ceramides become the new cholesterol? Cell Metabolism 27(2):276-280
- Chaurasia B, Holland WL, Summers SA (2018) Does this Schlank make me look fat. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism 29(9), 597-599
- Holland WL and Summers SA (2018) Strong Heart, Low Ceramides. Diabetes 67(8), 1457-1460
- Tippetts TS, Holland WL, and Summers SA (2018) The Ceramide Ratio: A Predictor of Cardiometabolic Risk. Journal of Lipid Research 59(9), 1549-1550
- Chaurasia B, Tippetts T, Monibas R, Liu J. Li Y, Wang L, Wilkerson J, Sweeney C.R, Pereira R, Sumida D, Maschek J. A., Cox J, Kaddai V, Lancaster G, Siddique M, Poss A, Pearson M, Satapati S, Zhou H, McLaren D, Previs S, Chen Y, Qian Y, Petrov A, Wu M, Shen X, Yao J, Nunes C, Howard A, Wang L, Erion M, Rutter J, Holland W, Kelley D, and Summers S. A. (2019) Targeting a Ceramide Double Bond Improves Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis. Science (in press)
- Summers SA, Chaurasia B, Holland WL (2019) Metabolic Messengers: Ceramides. Nature Metabolism (in press)
- Poss AM, Holland WL, Summers SA (2019) Risky Lipids. Refining the Ceramide Score that Measures Cardiovascular Health. European Heart Journal (in press)
- Poss AM, Maschek JA, Cox JE, Hauner BJ, Hopkins PN, Hunt SC, Holland WL, Summers SA*, and Playdon MC* (2019) Machine Learning Reveals Serum Sphingolipids as Cholesterol-Independent Biomarkers of Coronary Artery Disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation (in press) *The last two authors contributed equally
- Summers SA (2020) Ceramides: Nutrient Signals that Drive Hepatosteatosis. Journal of Lipid and Artherosclerosis 9(1), 50-65.
- Blitzer J, Wang L, and Summers SA (2020) DES1: A key driver of lipotoxicity in metabolic disease DNA and Cell Biology (in press)
